Major changes to the repairing standard, effective March 2024, focusing on the requirements for fire safety, fire alarms and carbon monoxide detectors in Scottish rental properties.
In response to the growing number of queries regarding these updates, we’ve compiled this informative blog post as part of a series of industry updates . Our aim is to assist landlords and property managers in understanding and implementing these changes effectively, while also offering our perspective on the most efficient solutions.
In part 1 we discussed changes to the electrical safety repairing standard.
In part 2 we covered updates for fixed heating in rented properties.
Understanding the updated Fire Alarm and Carbon Monoxide Detector requirements in Scottish rented properties.
In the following sections, we will delve into the crucial aspects of fire alarms and carbon monoxide detectors, with insights from our expert team and Mark Denholm, our Managing Director.
Fire Safety – installation requirements under the new Repairing Standard.
Living Room Alarms: A smoke alarm is now mandatory in the primary living space, typically the living room or lounge.
Circulation Space Alarms: Every circulation space, such as hallways and landings on each floor, must have a smoke alarm.
Kitchen Alarms: A heat alarm is required in every kitchen.
Mounting and Interlinking: All alarms should be ceiling-mounted and interlinked unless specific conditions apply.
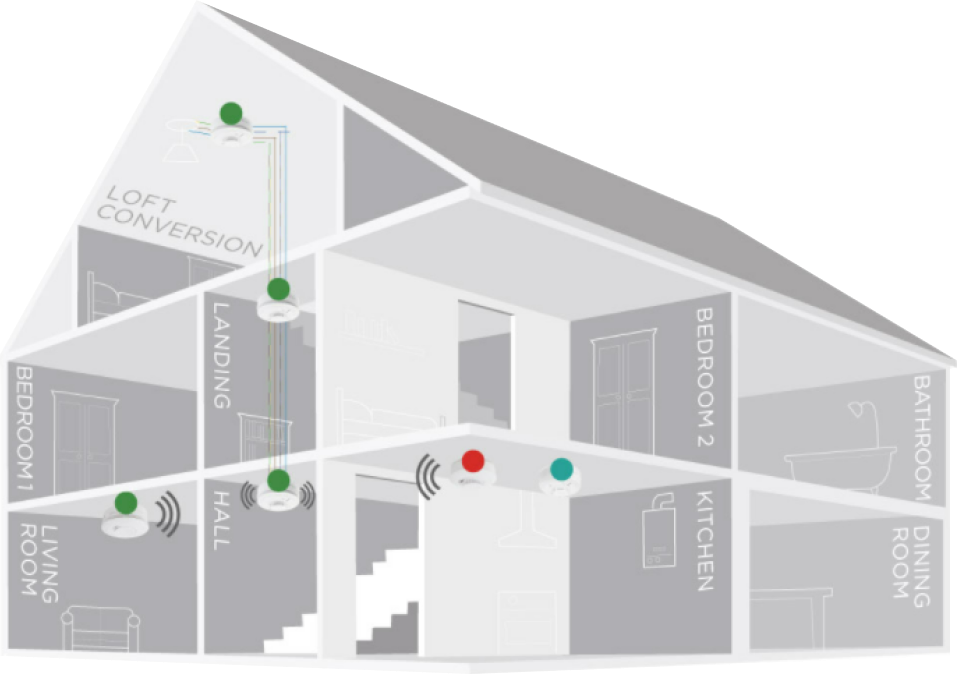
Basic requirements for Smoke Alarm installation in Edinburgh.
- Both mains-operated alarms (with battery backup) and tamper-proof long-life lithium battery alarms are acceptable.
- The lifespan of alarms should not exceed the manufacturer’s recommendation, usually up to 10 years. Units connected to the main power can include an additional backup supply for use during power cuts. Furthermore, alarms with wireless interlinking might have an independent power source for their radio signals. The use of replaceable batteries in these cases do not constitute a failure to meet the Repairing Standard.
- If you’re unsure about the requirements please click here to get booked in for a fire alarm test on your property.
Important fire safety factors to consider when positioning Smoke Alarms.
- For open-plan spaces that combine areas like kitchens and living rooms, a single alarm suffices, on the condition that it is positioned within 7.5 metres of any location within the room. The alarm selected must be suitable for the specific characteristics of the room.
- A “circulation space” refers to any area through which one must pass to access different parts of the house. However, this definition excludes the need for alarms in compact areas like vestibules, front porches, or half-landings that have little or no room for furnishings, storage, or appliances. For adequate warning in case of emergencies, an alarm should be installed on a landing or in a hallway, not exceeding 3 metres from the main bedroom’s entrance.
- Alarms mounted on walls must adhere to the manufacturer’s installation guidelines. These alarms need to be positioned no more than 30 cm from the ceiling’s highest point. Wall installation is advisable in cases of sloped or irregular ceilings, or to prevent disturbance of asbestos.
- Properties like HMOs might require smoke alarms to be mains wired interconnected either by means of cabling or wireless modules. HMO properties will also require additional protection, usually with a smoke alarm fitted in every room, including bedrooms and cupboards.
Fitting mains operated Smoke & Heat Alarms may require a Building Warrant.
Installation of mains-operated smoke/heat alarm systems may require a building warrant. Landlords are advised to consult their local Building Standards department. Additionally, the Scottish Fire and Rescue Service offers free home fire safety visits to assess risks and provide fire prevention advice.
The Repairing Standard for Carbon Monoxide (CO) detectors in Scottish rented properties.
With the updated standards, CO detectors are now required in:
1. All rooms housing fixed combustion appliances or flues.
A ‘combustion appliance’ is defined as a stationary unit, including items such as boilers, various types of fires (open fires included) and gas heaters, also for use with carbon-based energy sources like oil, solid fuels, or natural gas.
Please note the installation of carbon monoxide detectors is not required for gas cooking appliances such as cookers or hobs.
2. CO detectors must be either mains wired or have a long-life battery.
3. Placement of CO detectors should follow specific guidelines regarding ceiling or wall mounting, as outlined by the manufacturer.
Placement should be at a minimum distance of 300 mm from any wall for ceiling installations, except if specified differently by the manufacturer.
For wall installations, the device must be mounted no less than 150 mm beneath the ceiling and above the level of any doors or windows in the room, again, unless the manufacturer advises otherwise.
4. It’s important to use CO detectors only for the duration recommended by the manufacturer, typically up to a maximum of 10 years.
The expiration date should be noted on the detector, and it should be replaced before reaching this date. Additionally, the detector should include a feature that notifies users when it is nearing the end of its operational lifespan.
CO detector placement and compliance according to the Repairing Standard.
The Repairing Standard stipulates that CO detectors do not have to be connected with fire alarm systems; they can operate independently.
The Repairing Standard has provisions for adjustments in properties accommodating disabled individuals, including the installation of compatible deaf alerts.
Carbon monoxide detectors should be positioned within a range of 1 to 3 meters from the combustion appliance. It’s important to avoid placing these detectors in confined areas like cupboards. In cases where the appliance is situated within such an enclosed space, the detector must be installed at a suitable distance away from that area.
The repairing standard applies to spaces within the house designated for residential use. The absence of a carbon monoxide detector in non-residential areas like basements, attics, or garages does not constitute a violation of the Tolerable Standard.
Compliance with Scottish building regulations is compulsory when installing a new carbon-fuelled appliance or replacing an existing one.
Summary by Mark and the IES team.
We trust that the perspectives shared by Mark on the impact of the new repairing standard on fire alarms and carbon monoxide detectors in Scottish rental properties have been informative. As established Edinburgh electricians and experts in the installation of smoke, heat, and CO alarms in Edinburgh, our team is readily available to help with any questions or further details you may require.
If you’d like to book a full fire alarm test then click here.
You can find out more on the Scottish Government website here.
In part 4 of our Repairing Standard series we will cover water safety in Scottish rented properties .
Please don’t hesitate to get in touch with Lisa, Mark, or Chris for a chat about the choices available to you. Or, leave a comment below and we’ll respond here.

